Apache Access Log records incoming HTTP requests to the server, and the CustomLog directive defines what is kept in the log. The following is an example HTTP request, CustomLog directive, and the corresponding log that it captures:
GET /apache/log-post?field01=value01&field02=value02 HTTP/1.1 Host: simplified.guide Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %O \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" combined52.46.36.182 - - [30/Jan/2020:18:04:53 +0000] "GET /apache/log-post?field01=value01&field02=value02 HTTP/1.1" 200 13375 "-" "Amazon CloudFront"
The above CustomLog directive is sufficient if you're only logging GET requests, as, by default, Apache can log the HTTP request headers. POST data is sent in the request's body, so Apache can't log POST requests by default.
You can log POST request details by using dumpio module for Apache, which allows logging of HTTP request body.
Steps to log HTTP request body in Apache:
- Enable dumpio module for Apache.
$ sudo a2enmod dump_io #Ubuntu and Debian Enabling module dump_io. To activate the new configuration, you need to run: systemctl restart apache2 $ sudo a2enmod dumpio # SUSE
- Open Apache's configuration file using your preferred text editor.
$ sudo vi /etc/apache2/httpd.conf
- Turn on the related modules.
DumpIOInput On DumpIOOutput On
- Set the LogLevel to dumpio:trace7.
LogLevel dumpio:trace7

- Restart Apache for the changes to take effect.
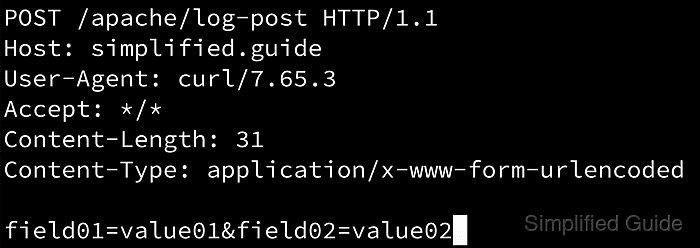
- Create an HTTP POST request with dummy data in the request body to test.
$ curl -XPOST --data "field01=value01&field02=value02" 127.0.0.1
- Check Apache's error log to see the logged HTTP request body.
$ sudo grep field01 /var/log/apache2/error.log [Sun Feb 02 01:46:13.062838 2020] [dumpio:trace7] [pid 21080] mod_dumpio.c(100): [client 127.0.0.1:47386] mod_dumpio: dumpio_in (data-HEAP): field01=value01&field02=value02


.png)
0 Comments